The U.S. Census Bureau conducted a National survey this year on behalf of the FDIC to ascertain the level of Unbanked and Underbanked households in the United States. The survey was designed to help the FDIC understand who is outside the banking system. The study which is the most comprehensive to date, reveals that just over a fourth (25.6 percent) of the households in the U.S. are unbanked or underbanked and those households are largely low-income and/or minority.
The survey additionally collected more accurate estimates of the Unbanked and Underbanked Households, and reasons why the people remain unbanked or underbanked. The survey estimates, represent the first time this kind of data has been collected in large metropolitan statistical areas (MSA), states, and across the nation.
"Access to an account at a federally insured institution provides households with an important first step toward achieving financial security - the opportunity to conduct basic financial transactions, save for emergency and long-term security needs, and access credit on affordable terms," stated Sheila Bair, Chairman of the FDIC. "By better understanding the households that make up this group - who they are and their reasons for being unbanked or underbanked, we will be better positioned to help them take that first step."
Terms
Unbanked is determined by households who answered "no" to the question "Do you or does anyone in your household currently have a checking or a savings account?"
Underbanked households were determined by those who have a checking or savings account but rely on alternative financial services. Specifically, using money orders, nonbank check-cashing services, payday loans, rent-to-own agreements, or pawn shops at least once or twice a year or tax refund anticipation loans at least once in the past five years.
Key Findings of the Study
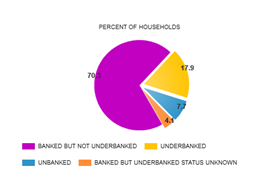
-
Of the households surveyed, 7.7 percent were unbanked, which translates nationally to 9 million households - approximately 17 million adults. An additional 17.9 percent - or 21 million households nationally (approximately 43 million adults) - were found to be underbanked.
- The proportion of U.S. households that are unbanked varies considerably across racial and ethnic groups with certain racial and ethnic groups being more likely to be unbanked than the population as a whole. Minorities more likely to be unbanked include blacks (21.7 percent of black households), Hispanics (19.3 percent), and American Indian/Alaskans (15.6 percent). Racial groups less likely to be unbanked are Asians (3.5 percent) and whites (3.3 percent).
- Certain racial and ethnic minorities are more likely to be underbanked than the population as a whole. Minorities more likely to be underbanked include blacks (an estimated 31.6 percent), American Indian/Alaskans (28.9 percent), and Hispanics (24.0 percent). Asians and whites are less likely to be underbanked (7.2 percent and 14.9 percent, respectively).
- Households with income under $30,000 account for at least 71 percent of unbanked households. As income increases, the share of households that are unbanked declines considerably. Nationally, nearly 20 percent of lower-income U.S. households - almost 7 million households earning below $30,000 per year - do not currently have a bank account. In contrast, only 4.2 percent of households with annual income between $30,000 and $50,000 and less than 1 percent of households with yearly income of $75,000 or higher are unbanked.
- Households with an annual income between $30,000 and $50,000 are almost as likely as lower-income households to be underbanked.
This survey goes hand in hand with a survey the FDIC conducted earlier in the year of bankers efforts to serve the unbanked and underbanked households in their community, see FDIC's Unbanked Survey. The survey is of such important information to the FDIC that they created a special website to display the findings at online at www.economicinclusion.gov.
It appears that the unbanked and underbanked households are close to the same number of estimates of those without proper medical insurance. Is there a correlation here? Is this something congress should be addressing - making sure that every American has proper banking and financial services?